

Sugar alcohols-their role in the modern world of sweeteners: A review. Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 17(2), 110–123 Noncardiac chest pain: Epidemiology, natural course and pathogenesis. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.

We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. In some cases, gallstones might be treatable with medication that may encourage the body to dissolve the stones over time. In worse cases, they may require antibiotics or time in the hospital. In most instances of food poisoning, a person can recover with home treatment, such as hydration and rest. Over-the-counter medications, such as bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol) may ease some indigestion symptoms.Ĭhronic conditions, for example, IBS, GERD, UC, or Crohn’s disease, may need to be treated with prescriptions from a doctor, though treatment will vary in each case. Medical treatment options are available to help with gas pain in the chest. Even a simple walk around the block may help. This could include carbonated drinks and sodas, milk and dairy products, and gluten.Įxercise may help gas to move through the digestive system to be eliminated. If the exact cause of gas pain in the chest is not known, it may be best to avoid any possible digestive triggers. Ginger products are available for purchase online, including chewable candies, drinks, and supplements. Research published in the European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology suggests that ginger can help with certain digestive symptoms.Ī small bit of the root may be eaten or made into ginger tea. Ginger root has traditionally been used to help with digestive issues. Warm water or herbal teas may help to ease pain and discomfort for some people. Drinking non-carbonated beverages will avoid extra gas intake. The following home remedies may help to ease the pain of excess gas in the chest:ĭrinking plenty of liquids can help to move excess gas through the digestive system, which can ease gas pain and discomfort. Treatment for gas pain in the chest often begins at home. Share on Pinterest Drinking ginger tea may help to relieve indigestion and other digestive symptoms. off-colored stools, often light or pale color.Gallbladder or biliary tree diseasesĪ condition in the gallbladder or biliary tree, such as gallstones, can cause chest pain and excess gas.

It is broken down by bacteria, resulting in gas. This excess production is because the fiber may stay in the gut for a longer time than other food components. While fiber-rich foods are beneficial for the digestive system, eating too much of a certain type of fiber can lead to excessive gas. Other problems in the digestive tract, such as those due to diabetes mellitus, can cause similar symptoms.Ĭhronic inflammatory conditions can also produce the following symptoms:
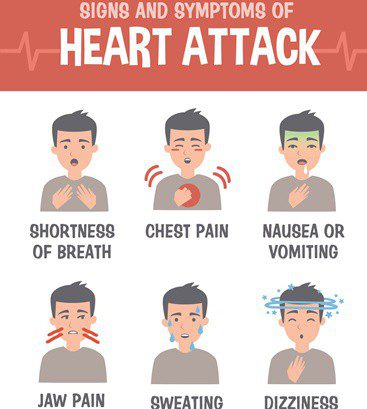
Inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn’s disease, may cause gas to build up in the digestive system. Digestive conditionsĬertain digestive conditions can lead to symptoms that resemble gas pain in the chest. Swallowing too much air can cause a buildup of gas in the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to gas pain in the chest or abdomen. Similarly to the carbon dioxide in fizzy drinks, the air we swallow when we eat, drink, or chew gum can become trapped in the digestive system. Too much of this gas can make a person burp, but it might also build up in the digestive tract and cause discomfort or pain. Excess carbonationĬarbonated drinks, for example, soda, tonic water, or sparkling water, have a fizz, provided by carbon dioxide gas. This pain often comes on quickly and can be experienced alongside other symptoms, including:Ī diet high in artificial sweeteners or sugar alcohols, such as sorbitol and xylitol, may cause digestive symptoms, including excess gas, in some people. Share on Pinterest Carbon dioxide gas from fizzy drinks can be a cause of chest pain.Įating contaminated food can cause food poisoning, which may also explain gas pain in the chest.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
